Publicly traded healthcare companies in the US reform ideas isn’t just a dry subject; it’s a dynamic arena where innovation, policy, and financial fortunes collide. Imagine a landscape populated by giants, from pharmaceutical powerhouses to managed care behemoths, all navigating a complex web of regulations and market forces. These companies, vital cogs in our nation’s health, are constantly evolving, adapting to shifts in consumer demands, technological advancements, and, of course, the ever-present specter of healthcare reform.
We’re going to delve into the current state of these companies, examining their core business models and the challenges they face. Then, we’ll explore the potential impact of proposed reforms, considering how these changes might reshape the industry and affect everything from drug pricing to access to care. We will also see how investors might be affected, and how companies could need to adjust their strategies.
The future of healthcare is being written now, and understanding these dynamics is more important than ever.
Examining the Current Landscape of Publicly Traded Healthcare Companies in the US
The US healthcare sector, a behemoth of the global economy, is dominated by publicly traded companies that shape the delivery of medical services, pharmaceuticals, and medical technology. Understanding this landscape is crucial for investors, policymakers, and anyone navigating the complexities of modern healthcare. These companies, with their diverse business models and significant market capitalizations, are constantly evolving in response to market pressures, regulatory changes, and consumer demands.
The following sections provide an overview of the key players, their challenges, and their diverse approaches to business.
Major Players and Market Capitalization
The US healthcare market is a landscape populated by industry giants, each with its own area of specialization and substantial market capitalization. Companies like UnitedHealth Group, a managed care behemoth, boast a market capitalization exceeding hundreds of billions of dollars, reflecting their vast reach and influence. Pharmaceutical giants such as Johnson & Johnson and Pfizer, with their portfolios of blockbuster drugs and medical devices, also command enormous market valuations.
These companies invest heavily in research and development, constantly seeking to innovate and bring new treatments to market. Medical device manufacturers like Medtronic and Abbott Laboratories, focusing on areas such as cardiovascular health and diabetes management, further contribute to the sector’s diversity. Each of these major players contributes significantly to the overall health and well-being of the nation, and their financial performance is closely watched by investors and analysts alike.
Current Challenges Faced by Healthcare Companies
The path to success in the US healthcare industry is paved with significant challenges. These companies must navigate a complex web of regulatory hurdles, intense market competition, and rapidly changing consumer expectations.One significant challenge is the ever-present threat ofregulatory scrutiny*. Companies are subject to rigorous oversight from agencies like the FDA and CMS, which can significantly impact product approvals, pricing, and reimbursement rates.
Any regulatory change can cause dramatic shifts in the market, and compliance costs are substantial. The potential for lawsuits and penalties adds further risk. For example, a drug approval delay or a change in Medicare reimbursement policies can directly impact a company’s revenue and profitability.Another major hurdle is the fiercemarket competition*. The healthcare sector is highly competitive, with numerous companies vying for market share in various segments.
Competition drives innovation, but it also puts downward pressure on prices and profit margins. Companies must differentiate themselves through product innovation, strategic partnerships, and efficient operations. This often involves expensive marketing campaigns and the constant need to adapt to new technologies and treatment approaches. The rise of biosimilars, for instance, has intensified competition in the pharmaceutical market.Finally, evolvingconsumer demands* present another set of challenges.
Patients are increasingly informed and empowered, seeking greater transparency, access to care, and personalized treatment options. Healthcare companies must adapt to these changing expectations by investing in patient-centric services, telehealth solutions, and digital health technologies. Failure to meet these demands can lead to decreased patient satisfaction, reduced market share, and negative brand perception. The growing emphasis on value-based care, where reimbursement is tied to outcomes, further underscores the need for companies to prioritize patient needs.
Diverse Business Models in Healthcare
The publicly traded healthcare companies employ a variety of business models to generate revenue and deliver healthcare services. The diversity of these approaches is a reflection of the complexity of the healthcare ecosystem.Here are some of the distinct business models:
- Managed Care: Companies like UnitedHealth Group and Anthem focus on managing healthcare costs and providing insurance coverage. They negotiate with providers, manage networks, and oversee utilization to control expenses.
- Pharmaceuticals: Companies such as Pfizer and Merck discover, develop, manufacture, and market prescription drugs. Their revenue is generated through drug sales and licensing agreements.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Companies like Medtronic and Abbott Laboratories design, manufacture, and sell medical devices, ranging from pacemakers to diagnostic equipment. Their revenue comes from device sales and related services.
- Healthcare Services: Companies like HCA Healthcare operate hospitals and outpatient facilities, providing direct patient care. Their revenue is generated through patient services and procedures.
- Biotechnology: Companies like Amgen and Gilead Sciences focus on the research, development, and commercialization of innovative biopharmaceutical products, often targeting complex diseases. Their revenue streams come from drug sales and royalties.
Investigating Proposed Reform Ideas Impacting Healthcare Businesses
The healthcare landscape in the United States is constantly evolving, and with it, the regulatory environment that shapes the operations of publicly traded healthcare companies. Understanding the potential impacts of proposed reforms is crucial for investors, healthcare professionals, and the general public. The following delves into several significant proposals currently under consideration, analyzing their potential effects on profitability, operational strategies, pricing, and access to care.
Specific Reform Proposals
Several key reform proposals are currently circulating within the US political landscape that directly affect publicly traded healthcare companies. These proposals aim to reshape various aspects of the healthcare industry, from drug pricing to insurance coverage and hospital operations.
- Negotiation of Prescription Drug Prices: This proposal, often advocated for by the government, would allow the government to negotiate directly with pharmaceutical companies for the prices of prescription drugs covered under Medicare. Currently, the government is largely prohibited from such negotiations.
The potential impact of this reform is significant. It could lead to lower drug prices, benefiting patients and reducing overall healthcare costs.
However, pharmaceutical companies might see a reduction in revenue, potentially impacting their profitability and investment in research and development. The exact impact depends on the scope of negotiation, the drugs included, and the degree of price reduction. A real-world example is the experience in other developed countries, such as Canada and the United Kingdom, where governments negotiate drug prices, resulting in lower costs but also potentially slower access to new medications.
- Expansion of Medicaid and/or Medicare: Proposals to expand Medicaid and/or Medicare eligibility are frequently discussed. These expansions could involve extending coverage to more individuals, potentially through increased income thresholds or the addition of new benefits.
This reform could significantly increase the number of insured individuals, leading to greater access to care.
For publicly traded healthcare companies, this could translate to increased patient volume and revenue, particularly for hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance providers. However, it could also put pressure on these entities to manage costs effectively, especially if reimbursement rates are not adjusted to account for the increased patient load. A relevant example is the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which expanded Medicaid and led to increased insurance coverage but also faced challenges in managing costs and ensuring access in some areas.
- Changes to Hospital Reimbursement Models: Proposals to alter how hospitals are reimbursed for services are also common. This might involve shifting from fee-for-service models (where hospitals are paid for each service provided) to value-based care models (where payments are tied to the quality and outcomes of care).
Value-based care aims to incentivize hospitals to improve patient outcomes and reduce unnecessary procedures.
This shift could significantly impact hospital profitability. Hospitals that excel at providing high-quality, cost-effective care could thrive, while those that struggle might face financial challenges. It also requires hospitals to invest in data analytics and care coordination to measure and improve outcomes. A case in point is the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) ongoing efforts to implement value-based care initiatives, which have demonstrated both successes and challenges in different healthcare settings.
Potential Impacts on Profitability and Operational Strategies
The following table provides a comparative analysis of the potential impacts of the proposed reforms on the profitability and operational strategies of various healthcare sectors.
| Reform Proposal | Pharmaceutical Companies | Hospitals | Insurance Providers | Medical Device Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negotiation of Prescription Drug Prices | Reduced revenue, potential impact on R&D investment, increased focus on cost-effectiveness of research. | Indirect impact through lower drug costs for patients and hospitals, potentially increasing patient access. | Indirect impact through lower drug costs for patients, which could lead to lower premiums. | Indirect impact, potentially influenced by changes in the types of treatments that are cost-effective. |
| Expansion of Medicaid and/or Medicare | Increased patient volume, potentially higher drug sales, but also pressure to manage costs. | Increased patient volume, potential for increased revenue, but also the need to manage costs effectively. | Increased enrollment, potentially higher premiums, but also increased risk and the need for efficient claims processing. | Increased demand for devices and services, assuming the expansions increase access to care. |
| Changes to Hospital Reimbursement Models | Indirect impact, influenced by hospital purchasing decisions and focus on value-based care. | Significant impact, with the potential for increased revenue if hospitals excel in value-based care; investment in data analytics is crucial. | Indirect impact, potentially influenced by the success of hospitals in managing costs and improving outcomes. | Indirect impact, as hospitals focus on value-based care, the demand for cost-effective devices and technologies may increase. |
Influence on Pricing Strategies and Access to Care
The proposed reforms are poised to significantly influence the pricing strategies and access to care provided by publicly traded healthcare entities. The potential outcomes are varied and complex.
- Pricing Strategies: Drug price negotiation could force pharmaceutical companies to lower prices, impacting their revenue and potentially leading to a shift in their research and development focus. Hospital reimbursement changes could incentivize hospitals to focus on providing cost-effective care, influencing the prices they charge for services. Insurance providers might adjust premiums based on changes in drug costs, hospital reimbursement rates, and the number of insured individuals.
- Access to Care: Drug price negotiation could improve access to essential medications, particularly for those with limited financial resources. Medicaid and/or Medicare expansions could broaden access to care for millions of Americans. However, changes to reimbursement models could also affect access. Hospitals that struggle to adapt to value-based care might reduce services or face financial constraints, potentially limiting access to care in certain areas.
Evaluating the Financial Implications of Healthcare Reform on Investors: Publicly Traded Healthcare Companies In The Us Reform Ideas
Healthcare reform is a constantly evolving landscape, and its impact on the financial performance of publicly traded healthcare companies is a crucial consideration for investors. Understanding how different reform proposals could affect stock prices is essential for making informed investment decisions. Let’s delve into how investors can navigate this complex environment.
Stock Performance Impacts of Reform Proposals
Different reform proposals can have vastly different effects on the stock performance of healthcare companies. For example, proposals focusing on increased price controls, such as those that would allow the government to negotiate drug prices, could significantly impact pharmaceutical companies.Consider the potential impact on a company like
- Pfizer (PFE)*. If the government successfully negotiates lower prices for its blockbuster drugs, the company’s revenue and earnings could decline, potentially leading to a decrease in its stock price. Conversely, companies focused on value-based care, such as
- UnitedHealth Group (UNH)*, might benefit from reforms that incentivize cost-effective care. If reforms promote value-based care models, UnitedHealth’s stock could see a boost due to its strong position in this area. Another example involves hospital systems. Proposals focusing on expanding health insurance coverage, like the Affordable Care Act (ACA), could lead to an increase in patient volume for hospitals like
- HCA Healthcare (HCA)*. However, the specific impact depends on the details of the reform, including the level of reimbursement rates. A decrease in reimbursement rates could negatively impact the company’s profitability, despite the increase in patient volume.
Key Metrics for Assessing Healthcare Reform’s Impact
Investors need to consider specific metrics when assessing the potential impact of healthcare reform on their portfolios. These metrics provide crucial insights into a company’s financial health and its ability to weather reform changes.
- Revenue Growth: Evaluate how proposed reforms could affect a company’s revenue streams. Will price controls or changes in coverage impact sales volume? Consider the following formula:
Revenue Growth = ((Current Period Revenue – Prior Period Revenue) / Prior Period Revenue)
– 100. Investors should look for companies with diversified revenue streams to mitigate risks.
- Gross Margin: This metric indicates a company’s profitability after accounting for the direct costs of producing goods or services. Price controls and changes in reimbursement rates can directly affect a company’s gross margin. Analyze the company’s cost structure and its ability to manage costs effectively.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): EPS reflects a company’s profitability on a per-share basis. It is a critical indicator of a company’s financial health and how changes in revenue, cost, and taxation may affect investors. Investors can use this formula to estimate the EPS:
EPS = (Net Income – Dividends on Preferred Stock) / Weighted Average Number of Shares Outstanding
.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio measures a company’s financial leverage and its ability to meet its financial obligations. Companies with high debt levels may be more vulnerable to economic downturns and changes in reimbursement rates. Analyze a company’s balance sheet to determine its debt-to-equity ratio.
Adapting Investment Strategies for Healthcare Reform
Navigating the uncertainties of healthcare reform requires investors to adopt flexible and proactive investment strategies. Here’s how investors can adapt.Investors should conduct thorough research on proposed reforms and their potential impact on specific companies. This includes analyzing policy proposals, reading expert analysis, and monitoring industry trends. Diversification is key to mitigating risk. Spreading investments across different healthcare sectors, such as pharmaceuticals, hospitals, and managed care, can reduce the impact of any single reform.
Investors should consider investing in companies that are well-positioned to adapt to changing market conditions. This includes companies with strong balance sheets, diversified product portfolios, and a focus on innovation. Regularly review and adjust investment portfolios. The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, so investors need to stay informed and be prepared to adapt their strategies as needed.
Analyzing the Operational Adjustments for Healthcare Companies in Response to Reform
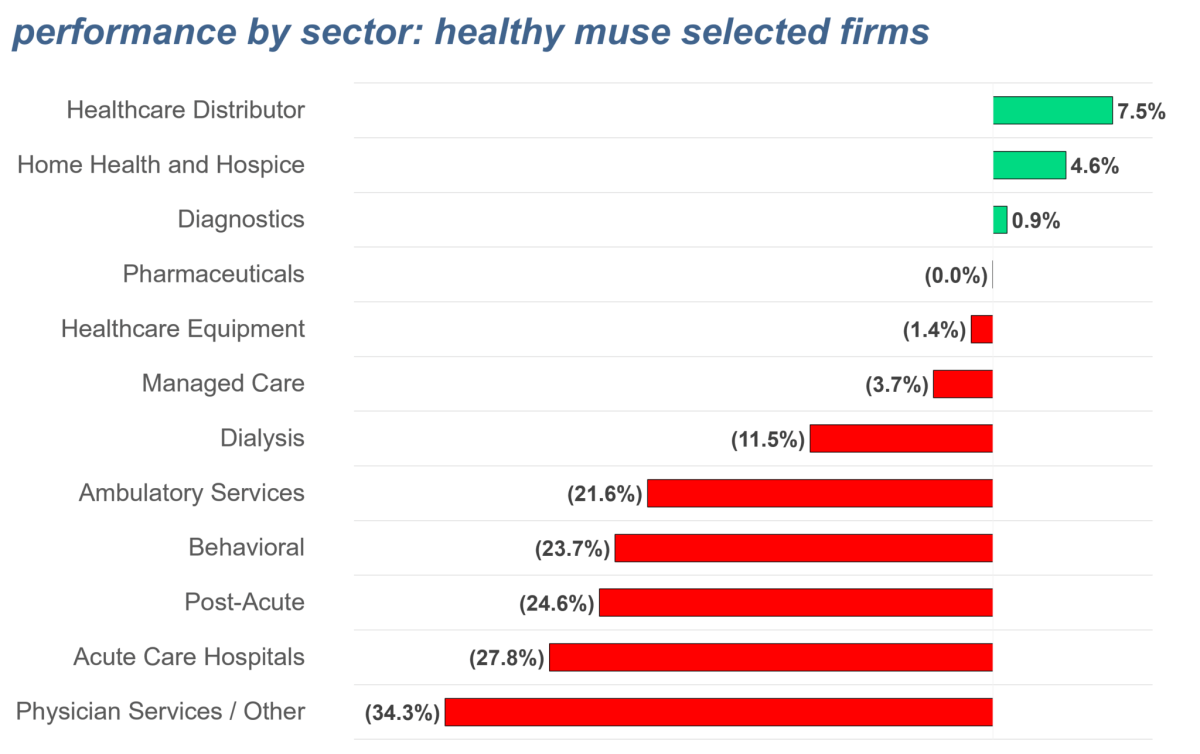
Source: thehealthymuse.com
Healthcare reform isn’t just about policy; it’s a catalyst for transformation within the industry. Publicly traded healthcare companies must proactively adapt their operations to navigate the evolving landscape and maintain their financial health while fulfilling their core mission: patient care. This involves a deep dive into every aspect of their business, from the supply chain to the technology they employ.
Changes to Supply Chains, Staffing, and Technology, Publicly traded healthcare companies in the us reform ideas
The success of healthcare companies hinges on their ability to adjust their operational structure. This means significant changes to supply chains, staffing models, and technological infrastructure.
- Supply Chain Adaptations: Reform can lead to shifts in drug pricing, increased demand for certain services, and changes in reimbursement models. Companies may need to:
- Diversify suppliers to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependencies and potential disruptions.
- Implement just-in-time inventory management to reduce waste and costs, particularly for pharmaceuticals with expiration dates.
- Negotiate aggressively with suppliers to secure favorable pricing, given the potential for reduced revenue streams.
- Staffing Model Adjustments: Healthcare reform can necessitate changes in staffing to align with new service demands, regulatory requirements, and cost-containment strategies.
- Employ a multidisciplinary team approach, incorporating roles such as case managers, patient navigators, and telehealth specialists.
- Invest in training and upskilling programs for existing staff to enhance their competencies in areas such as value-based care and electronic health records.
- Optimize staffing levels to meet patient needs while controlling labor costs.
- Technological Infrastructure Updates: Embracing technology is critical for streamlining operations, improving patient care, and complying with new regulations.
- Invest in interoperable electronic health records (EHR) systems to facilitate seamless data exchange between providers and enhance care coordination.
- Implement telehealth solutions to expand access to care, reduce costs, and improve patient satisfaction.
- Utilize data analytics to identify areas for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and personalize patient care.
Successful Adaptation Strategies from Previous Reform Efforts
History provides valuable lessons. Healthcare companies that have successfully navigated past reform efforts offer compelling examples of how to adapt.
Example 1: The Rise of Integrated Delivery Networks (IDNs) following the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Many hospitals and health systems merged or formed partnerships to create IDNs. These networks offered a continuum of care, from primary care to specialized services, allowing them to manage patient populations more effectively and participate in value-based care models. This integrated approach allowed these entities to improve efficiency and control costs.
Example 2: Emphasis on Preventative Care after Medicare’s Expansion. Some companies prioritized preventive care and wellness programs to proactively manage patient health. This resulted in lower long-term costs and better patient outcomes, while aligning with the evolving reimbursement landscape.
Ethical Considerations and Social Responsibilities During Reform
Healthcare companies hold a profound responsibility, especially during times of reform. It’s a time when ethical considerations and social responsibilities must be at the forefront.The focus on patient care must be unwavering. This involves prioritizing access to quality care, regardless of a patient’s socioeconomic status or insurance coverage. Companies must ensure that cost-cutting measures do not compromise the quality of care or negatively impact patient outcomes.
Transparency in pricing and billing practices is also crucial to build trust with patients and the public.Community outreach is a cornerstone of social responsibility. Healthcare companies should actively engage with the communities they serve. This includes providing health education, supporting community health initiatives, and addressing health disparities. Collaboration with community organizations can help companies better understand and meet the needs of the populations they serve.
Forecasting the Future of Publicly Traded Healthcare Companies Under Reform

Source: webflow.com
Navigating the evolving healthcare landscape requires a forward-thinking approach. Predicting the trajectory of publicly traded healthcare companies necessitates a deep understanding of potential reform scenarios and their subsequent impacts. This analysis offers a glimpse into the future, considering the strategic adaptations and technological advancements shaping the industry.
Market Dynamics in Reform Scenarios
The future of publicly traded healthcare companies hinges on the specific contours of healthcare reform. Several potential scenarios exist, each triggering distinct shifts in market dynamics.
- Scenario 1: Expanded Coverage & Increased Regulation: Under this scenario, we can anticipate a surge in demand for healthcare services, particularly for preventative care and chronic disease management. Companies focusing on these areas, such as UnitedHealth Group (UNH) and CVS Health (CVS), could experience substantial growth. However, increased regulation, including price controls and stricter oversight of pharmaceutical pricing, might squeeze profit margins. The implementation of value-based care models, rewarding quality and efficiency, will necessitate significant operational adjustments for hospitals and health systems, leading to potential consolidation and strategic partnerships.
- Scenario 2: Market-Based Reforms & Consumer Choice: This approach prioritizes consumer choice and market competition. Healthcare companies offering innovative insurance products, such as high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) and health savings accounts (HSAs), could thrive. Companies like Anthem (ANTM) that emphasize consumer empowerment and price transparency might gain a competitive advantage. However, this scenario also poses risks, including increased price volatility and the potential for adverse selection, where healthier individuals opt out of insurance, leading to higher premiums for the remaining insured population.
Pharmaceutical companies might face increased scrutiny of drug pricing and competition from generic drugs, impacting profitability.
- Scenario 3: Single-Payer System: The implementation of a single-payer system, often referred to as “Medicare for All,” would fundamentally reshape the healthcare industry. While this scenario could ensure universal coverage, it would likely lead to significant changes in reimbursement rates and the role of private insurance companies. Hospitals and healthcare providers could face reduced revenues, necessitating cost-cutting measures and operational efficiencies. Pharmaceutical companies might experience downward pressure on drug prices.
Companies with strong bargaining power and operational efficiency, such as Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) and Roche (RHHBY), could be better positioned to weather the storm.
The financial health of companies will vary depending on the reforms enacted. Companies like Teladoc Health (TDOC) could see significant gains due to increased access to telehealth services. Companies with diversified portfolios, such as a company like Abbott (ABT) with their range of diagnostic tests and medical devices, might be more resilient to shifts in any specific segment. Mergers and acquisitions are expected to continue, with companies seeking to gain market share, expand service offerings, and achieve economies of scale.
The companies that adapt quickly to changing market conditions, embrace innovation, and prioritize consumer needs will be the most successful.
Role of Innovation and Technological Advancements
Innovation and technological advancements are poised to revolutionize the healthcare landscape, profoundly impacting publicly traded healthcare companies. These advancements offer opportunities to enhance efficiency, improve patient outcomes, and drive down costs.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics, drug discovery, and personalized medicine is rapidly accelerating. Companies investing heavily in AI, like Intuitive Surgical (ISRG) with their da Vinci surgical systems, are expected to gain a significant advantage.
Telehealth, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, will continue to expand, enabling remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, and improved access to care, particularly in underserved areas. Data analytics and predictive modeling will play a crucial role in identifying high-risk patients, optimizing treatment plans, and preventing hospital readmissions.
- Personalized Medicine: This approach tailors medical treatment to individual patient characteristics, such as genetic makeup and lifestyle. Companies that invest in genomic sequencing and targeted therapies will likely experience substantial growth.
- Digital Health: The use of mobile apps, wearable devices, and remote monitoring systems is transforming healthcare delivery. Companies offering these technologies can improve patient engagement, track health metrics, and provide real-time feedback.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain has the potential to enhance data security, streamline administrative processes, and improve supply chain management in the healthcare industry.
These advancements will reshape the competitive landscape. Companies that successfully integrate these technologies into their operations will gain a competitive edge. The ability to adapt to and leverage these innovations will be a key determinant of success for publicly traded healthcare companies in the years to come. Consider the rise of companies like 23andMe (ME), who have built their business on direct-to-consumer genetic testing, illustrating the potential of innovation in the industry.
Summary
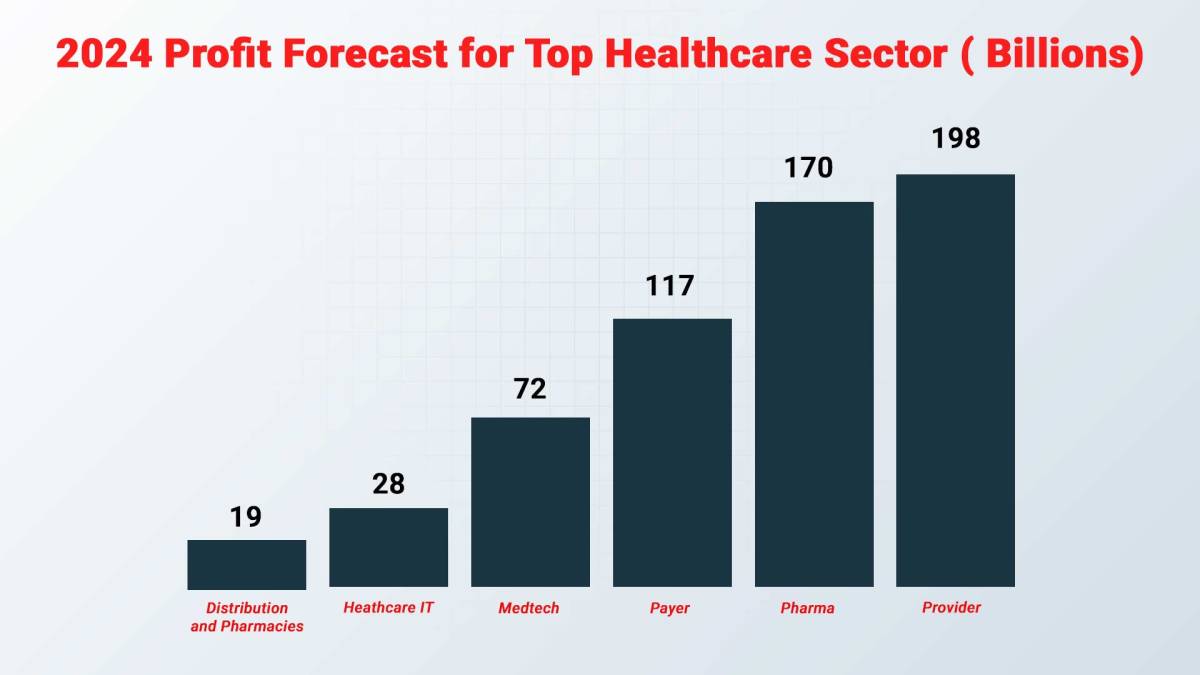
Source: targetnxt.com
In conclusion, the journey through the world of publicly traded healthcare companies and the potential impacts of reform is a fascinating one. We’ve seen how these companies are adapting, how investors are reacting, and how the future of healthcare is being shaped. Remember, the ability to anticipate and adapt to change is key. It’s a call to action, urging us to stay informed, engage in meaningful conversations, and support policies that foster both innovation and equitable access to healthcare for all.
The healthcare industry is complex, but it is an industry that is worth the attention of all.